
Risk Management Standards (Image by AspenHR)

Risk Management Standards (Image by AspenHR)
Risk management standards, particularly in the context of business and IT, are crucial guidelines that help organizations identify, assess, and manage risks effectively. The most recognized among these is the ISO 31000 standard for risk management.
These ISO 31000:2018 standards serve as a roadmap for businesses to navigate through potential risks, ensuring that every possible threat is identified, analyzed, and managed appropriately.
This adherence not only safeguards the organization against unforeseen hazards but also boosts stakeholder confidence by demonstrating a commitment to best practices in risk management.
Now, let’s talk about a key play in risk management: deciding when to pass the ball, or in our terms, transferring a risk. This usually happens in the risk response phase.
This phase is where you weigh your options on how to deal with risks. Often, it’s like choosing to hand off certain risks to someone else, say through insurance or by outsourcing.
If you are interested in learning more about risk management standards, we are eager to hear from you. Let’s look into it further and find out more insights together.
The main goal of risk management framework standards is to keep things running smoothly, even when surprises pop up.
Risk management standard is about proactively managing uncertainty, making informed decisions, and building a more resilient organization.
And here’s a cool part: these standards aren’t just about avoiding the bad stuff. They also help you grab opportunities.
Finally, these standards are all about trust. When customers and partners see that you’re managing risks like a pro, they’re more likely to trust you with their business.
When we talk about the primary risk management standards, we’re focusing on a few key frameworks that help organizations stay on top of potential risks.
These standards are like the rules of the game for managing uncertainties effectively. First, there’s ISO 31000.
This ISO 31000 is a broad-spectrum framework that offers guidelines for risk management applicable across various industries.
ISO 31000 is a universal handbook for identifying, assessing, and managing risks in any business context.
Next up, we have the COSO ERM Framework. This one integrates risk management with enterprise governance.
COSO ERM Framework is particularly handy for aligning risk management strategies with business goals, ensuring that every decision takes potential risks into account.
Then there’s NIST SP 800-30, a standard that’s especially relevant in the IT realm. NIST SP 800-30 focuses on IT risk management, providing a structured approach to identifying, assessing, and responding to IT-related risks.
ISO/IEC 27001 is another key player. This standard zeroes in on information security management. It’s all about keeping a company’s information assets secure, a must in our digital age.
For those involved in project management, the Project Management Institute (PMI) Risk Management Framework is a go-to.
PMI Risk Management Framework offers specific guidelines for managing risks within project environments, ensuring projects stay on track despite the uncertainties.
Lastly, AS/NZS ISO 31000 is the Australian/New Zealand adaptation of ISO 31000. It maintains the core principles of risk management while addressing local needs.
Those primary risk management standards provide a structured way to deal with risks.
They guide you through spotting potential troubles, understanding what they could mean, and then figuring out the best way to dodge or lessen their impact.
Now, deciding which standard to use can feel like choosing your favorite ice cream flavor. The good news is, you don’t have to pick just one.
Those standards can team up, working together to cover all your bases, making sure you’re ready for any risk that comes knocking.
It’s not about picking one over the other. Many businesses mix and match parts of these standards to tailor-make a strategy that fits their unique situation like a glove.
The main goal? To equip yourself with a strategy that lets you manage risks smartly and confidently, navigating the unpredictable seas of business with ease.
Alright, let’s dive a bit deeper into each of these standards. We’ll take a closer look at what makes them tick and how they help businesses and IT organizations keep a handle on their risks.
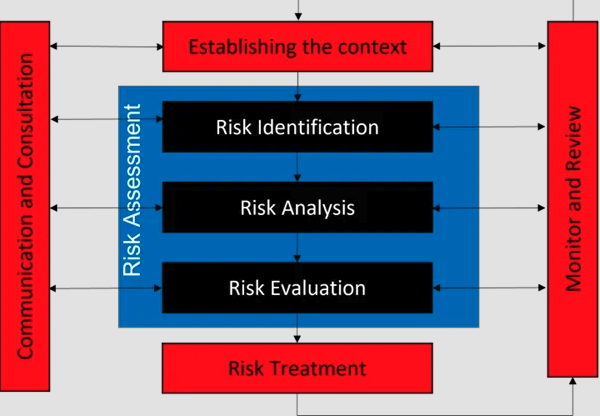
ISO 31000 is a standard that sets the tone for effective risk management. It’s designed to be used by any organization, no matter the size or sector.
The core of ISO 31000 revolves around a set of principles. These are the building blocks for a solid risk management framework.
ISO 31000 is built on a foundation of key principles. These principles aren’t just guidelines; they’re the nuts and bolts that hold together a robust risk management strategy.
ISO 31000 highlights the importance of weaving risk management into the fabric of organizational processes and decision making.
The ISO 31000 standards aim to address uncertainty directly by using a systematic approach that relies on the best available information and can be customized to fit your organization.
The ISO 31000 standards are also about considering the human side of things, being open and inclusive, ready to adapt, and always aiming to get better.
In addition to these principles, ISO 31000 provides guidelines for setting up a risk management framework.
This framework is all about ensuring that risk management is an integral part of the organization’s governance, with the right policies and procedures in place.
That’s why You get guidance on how to set up, run, check, and enhance your risk management strategies across the board.
The ISO 31000 standard about nurturing a culture where being aware of and ready for risks is just part of what you do. It’s a continuous journey, evolving as your business and the world around it change.
Organizations can avoid pitfalls and seize opportunities by following ISO 31000 to manage risks effectively.
The COSO ERM Framework, crafted by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission, really stands out in the risk management arena
The COSO ERM Framework is like the master weaver, helping you weave risk management seamlessly into the very fabric of your organization.
What makes COSO ERM unique? It’s all about syncing risk management with your organization’s aims and ambitions.
It’s not just about steering clear of risks; it’s about smart risk-taking as part of your strategy and decision-making process.
This framework reshapes the way businesses view risk management. It’s not just a shield against threats; it’s a tool to reach your goals.
With COSO ERM, risk management becomes a strategic ally, helping you move through uncertainty with more assurance and paving the way for lasting success.
COSO ERM isn’t a rigid set of rules. It’s more like a versatile toolkit, with components like governance, risk assessment, and response, internal control activities, and more.
Those elements work together to create a comprehensive approach to managing risks.
Each organization can customize the COSO ERM Framework to meet its specific needs and situation.
Yes, the framework is adaptable, allowing for molding to fit the contours of the organization.
This flexibility makes COSO ERM a valuable asset for managing risks effectively while pursuing strategic goals.
NIST SP 800-30 comes straight from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), and it’s a big player in the realm of information security risk management.
NIST SP 800-30 acts as your detailed how-to manual for navigating the complex world of cyber risks.
This SP 800-30 guide breaks down how to do thorough risk assessments for your information systems, step by step.
One of the coolest things about NIST SP 800-30 is how it champions customizing these risk assessments.
NIST SP 800-30 knows that every organization is unique, so it guides you in adapting the process to fit your specific situation and needs.
The guide walks you through spotting potential cyber threats and weak spots, sizing up how likely and impactful these threats could be, and then helping you sort them by how risky they are.
Yes, NIST SP 800-30 gives you the know-how to focus your defense where it counts most. So, in a world where cyber threats are always changing, having NIST SP 800-30 in your corner is crucial.
NIST SP 800-30 is a key resource for any organization that wants to protect its digital treasures against the latest and greatest in cyber risks.
ISO/IEC 27001 is a top-tier standard in the world of Information Security Management Systems (ISMS). It’s the go-to framework for organizations looking to safeguard their information assets.
This ISO/IEC 27001 standard is all about setting up a system that ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information – (CIA) of your information assets.
So, what exactly is ISO/IEC 27001? It’s more than just a checklist; it’s a comprehensive framework that guides you in setting up, rolling out, and maintaining an ISMS that really works.
This includes policies, procedures, technical measures, and people management strategies.
The standard is super relevant in today’s digital age, where information is as valuable as gold.
It helps organizations protect sensitive data from cyber threats, unauthorized access, and data breaches.
ISO/IEC 27001 is not just a standard, but a strategic investment. In a world where data breaches can cost millions and harm reputations.
The Project Management Institute (PMI) Risk Management Framework is a specialized guide designed for integrating risk management into the project management process.
Developed by the Project Management Institute (PMI), this framework offers a structured and proven approach for integrating risk management into every stage of your project lifecycle.
This framework provides a step-by-step approach, showing you how to spot, assess, manage, and keep an eye on risks throughout your project’s journey.
PMI Risk Management Framework also about spotting the silver linings, the opportunities that come disguised as risks.
Acting like a trusty navigator, this framework integrates seamlessly into the broader project management process.
PMI Risk Management Framework systematically guides you through identifying risks, evaluating them, strategizing responses, and continuously monitoring these risks as your project evolves.
You can make risk a central part of your project planning process, rather than an afterthought, by using the PMI framework.
This method equips project teams to be more resilient, make smarter decisions, and greatly boosts the chances of your project’s success.
AS/NZS ISO 31000 is the Australian/New Zealand adaptation of the globally recognized ISO 31000 risk management standard.
AS/NZS ISO 31000 is like the local flavor of the renowned ISO 31000 risk management standard.
This regional adaptation of the global standard, AS/NZS ISO 31000, offers a tailored approach, fitting the unique business landscapes and regulatory frameworks of Australia and New Zealand.
The beauty of AS/NZS ISO 31000 is in its versatility. Whether you’re running a small startup or steering a large enterprise, this standard has got you covered.
AS/NZS ISO 31000 is adaptable across various sectors, making it a valuable asset for any business type.
AS/NZS ISO 31000 also fosters a culture where risk management is part of the everyday business strategy.
Moreover, AS/NZS ISO 31000 emphasizes the importance of integrating risk consideration into every decision you make.
This means that every move your business makes is backed by a solid understanding of the risks involved and the potential benefits.
The most common risk management standards are essentially frameworks that help businesses and IT organizations handle risks effectively.
Leading the pack is ISO 31000. Another key standard is the COSO ERM Framework.
For IT-specific risks, there’s NIST SP 800-30, which offers a detailed approach for managing IT risks, and ISO/IEC 27001, focusing on information security management.
In project management, the PMI Risk Management Framework stands out. Lastly, region-specific standards like AS/NZS ISO 31000 adapt the global guidelines to fit the unique contexts of Australia and New Zealand.
All these standards share a common goal: to help organizations proactively manage risks, ensuring smooth operations and the achievement of business goals.
Deciding whether COSO or ISO 31000 is better isn’t a matter of one being universally superior. Because, it’s about what fits best with your organization’s needs.
So, there’s no clear winner in the “COSO vs. ISO 31000” battle.
ISO 31000 is a globally recognized standard, offering a broad, flexible framework for risk management applicable to any organization, regardless of type or size.
On the other hand, the COSO ERM Framework is more focused on integrating risk management with enterprise governance and internal control.
So, if you’re seeking a general, globally applicable framework, ISO 31000 might be your go-to.
But if you want something that ties closely into enterprise governance and internal controls, COSO could be more suitable.
Current risk management standards are built around seven crucial elements:
These elements form the backbone of effective risk management, guiding organizations in proactively managing risks and ensuring informed decision-making.