
Types of Security Incident Management and How to Handle (Image by EAB)

Types of Security Incident Management and How to Handle (Image by EAB)
Types of security incident management include network breaches, where unauthorized users gain access; malware attacks, where malicious software is introduced; and data theft, where sensitive information is illegally copied or stolen.
Each type requires a tailored response strategy. These types will vary because Security Incident Management (SIM) is a critical practice that addresses various disruptions that can compromise information security.
But remember, these different types work together in a well-coordinated team addressing multiple threats.
The best practice is to be prepared: have a response team in place, conduct regular training, and keep security systems up to date. This proactive approach minimizes damage and helps you quickly return to normal operations.
In this article, we’ll try to understand the different types of SIMs and how to manage them.
Our objective is to empower you to maintain your business’ integrity and reliability. So, let’s talk about the types of SIMs.
The types of security incidents that businesses encounter are varied and sophisticated, each with its unique challenges and potential impacts.
The variety of threats requires a vigilant and multi-faceted approach to the broad context of IT incident management. Knowing each of these threats is just the beginning.
Security incident management often confronts malware and ransomware, a formidable threat to data integrity and availability.
Malware, software designed to damage or disable, can infiltrate systems, stealing or corrupting data.
Ransomware, a more aggressive form, encrypts data, demanding payment for release. Both disrupt business operations, with ransomware posing an additional financial threat.
The key lies in robust security systems to detect and neutralize these threats promptly, minimizing impact and restoring normal operations swiftly.
Phishing and social engineering attacks manipulate individuals into revealing sensitive information.
These incidents exploit human vulnerabilities rather than system weaknesses. Effective management involves extensive user awareness training, ensuring employees can recognize and report such attempts.
This human-centric approach to security is vital as even the most advanced technical defenses can be undermined by a single misled click.
Incidents of unauthorized access and network intrusions are a constant challenge in every IT incident management.
These breaches occur when individuals gain access to systems without permission, leading to potential data leaks or theft.
The risks extend beyond immediate data loss, including long-term reputational damage and legal consequences.
Proactive monitoring and strict access controls are crucial to prevent such incidents and mitigate their impact when they occur.
Insider threat attacks involve individuals within the organization misusing access to harm the company.
These can be intentional, like data theft for personal gain, or unintentional, resulting from negligence.
The complexity of insider threats requires a multi-faceted approach, combining strict access controls, continuous monitoring, and employee training. Recognizing and managing these threats is vital for protecting sensitive information and maintaining trust.
Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks are where interceptors secretly relay or alter communication between two parties.
These incidents can lead to data breaches, eavesdropping, or session hijacking. MitM attacks, often difficult to detect, require advanced encryption and authentication protocols for prevention.
Regular system audits and secure communication channels are essential in managing these threats.
Remember, these digital threats are not isolated incidents. They can intertwine and amplify each other, creating a cascading effect that disrupts your entire operation.
For instance, a phishing attack might open the door to malware, or an insider threat could facilitate unauthorized access.
This interconnected nature demands a comprehensive, integrated approach to security incident management, ensuring that addressing one threat doesn’t inadvertently expose another.
Failing to recognize these links can lead to operational chaos, severely disrupting business continuity.
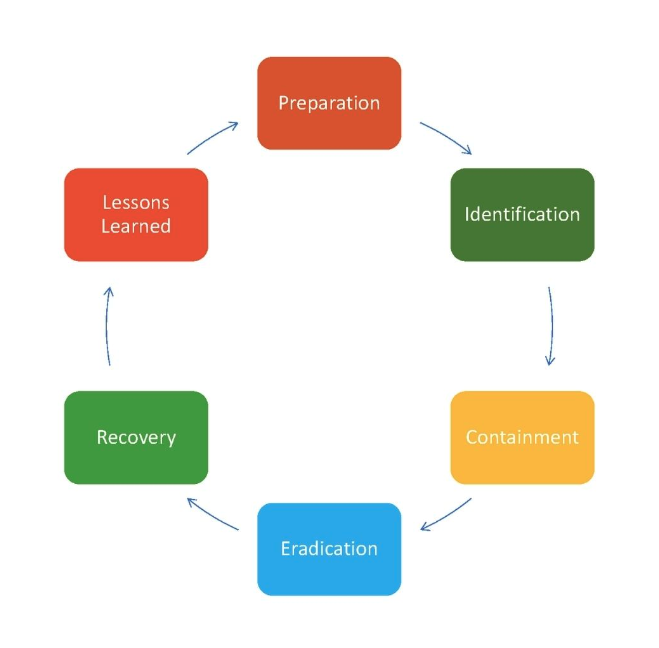
In addressing the complex interrelationships of security incidents, a holistic approach is critical.
Because the ideal security incident management mindset is not just about patching holes. SIM is about creating a resilient environment that anticipates and mitigates risk from multiple angles.
For handling malware and ransomware, the first line of defense is robust, up-to-date antivirus software.
This software should be complemented by regular system backups, ensuring data can be restored in the event of an attack. But technology alone isn’t enough.
Employee education is crucial – staff should be trained to recognize suspicious emails and websites that often serve as entry points for malicious software.
Phishing and social engineering attacks exploit human vulnerabilities, making awareness training equally important here.
Employees should be taught to scrutinize emails for signs of phishing and verify the authenticity of requests for sensitive information.
A culture of security mindfulness, where employees feel comfortable questioning and reporting potential threats, goes a long way.
When it comes to unauthorized access and intrusions, strong password policies and two-factor authentication play a vital role.
Regularly reviewing and limiting access privileges ensures that individuals can only access the information necessary for their roles.
Network monitoring tools can also detect unusual access patterns, alerting administrators to potential breaches.
Addressing insider threats requires a balance of technology and trust. Regular audits and monitoring of user activities help in detecting unusual behavior that may indicate a threat.
Concurrently, fostering a positive work environment reduces the likelihood of malicious insider actions.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks necessitate secure, encrypted communication channels. Using VPNs and SSL protocols can help ensure that data remains private and unaltered during transmission.
That is why regular security assessments and incident response exercises can help your organization understand how one vulnerability can open the door to another.
The key objective is to ensure that you have a comprehensive response strategy that takes into account the multi-faceted nature of these threats.
This proactive, integrated approach is essential to creating a secure IT environment that can withstand the evolving digital threat landscape.
In summing up our journey, it’s clear the SIM landscape is not just a technical challenge, but a dynamic puzzle that intertwines technology, human behavior, and organizational culture.
The types of threats – from malware to insider attacks – are as varied as they are sophisticated, each requiring a nuanced approach.
The key takeaway is the need for a proactive, holistic strategy. This involves not only deploying robust technological defenses but also fostering a culture of awareness and vigilance among employees.
As the digital world evolves, so do the threats, making continuous learning and adaptation essential.
Understanding and managing these various security incidents is not just about protecting data; it’s about safeguarding the trust and integrity of the entire organization.
So, as we look to the future, let’s embrace the holistic approach to address different types of security incident management with confidence based on knowledge and proper preparation.