
Why IT Service Management Important (Image by Enterpreneur)

Why IT Service Management Important (Image by Enterpreneur)
What is IT service management? How does it work? Why is IT service management (ITSM) important? What are the benefits of IT management services? What are some common IT management services?
First, IT service management is a framework that aligns IT services with business objectives, streamlining IT operations for efficiency and effectiveness.
ITSM emphasises a service-centric and process-oriented approach, ensuring that IT functions support business goals and satisfy customer needs.
ITSM is crucial because it aligns IT services with business objectives, ensuring that IT operations efficiently support the overall goals and strategies of the organisation.
This alignment is crucial for the smooth functioning of business processes, enhancing productivity, and reducing costs associated with IT services.
Successful ITSM implementation involves various critical factors, including managerial support, employee engagement, clear communication, and a well-structured approach to process improvement.
Research by Serrano, J.; Faustino, J.; Adriano, D.; Pereira, R.; and da Silva, M.M. shows how ITSM models and standards have been created for the implementation and evaluation of processes, with ITIL being the most adopted framework by IT organisations.
ITIL is the most widely adopted framework, but other frameworks and standards, such as the Microsoft Operation Framework (MOF), the Capability Maturity Model Integration for Services (CMMI-SVC), and the ITSM leading standard ISO/IEC 20,000, have also been developed and applied.
These improvements increase client satisfaction, productivity gains, and cost reduction.
Therefore, ITSM’s integral role in optimising IT operations is undeniable, as it directly contributes to a company’s overall performance and strategic objectives.
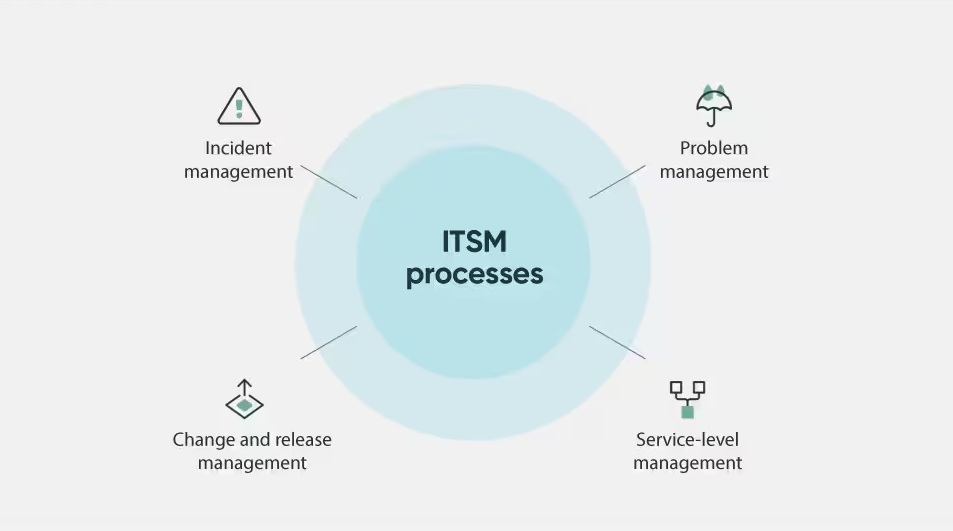
IT Service Management (ITSM) processes, such as incident management, change management, and service desk operations, are fundamental in how ITSM works to align IT services with business objectives.
These processes ensure efficient and effective delivery and support of IT services.
These ITSM processes create a stable and responsive IT environment, aligning IT operations with business needs and improving overall service delivery.
The service desk is the central hub for ITSM activities, handling incidents and requests and acting as users’ primary point of contact.
The service desk covers many functions, including incident management, problem management, change management, and knowledge management.
The Service Desk streamlines communication between IT and users by providing a single point of contact, ensuring efficient management of IT requests and issues.
It plays a significant role in enhancing user experience through quick problem resolution and feedback loops, ultimately leading to increased productivity and cost savings for the organisation.
The Service Desk’s ability to handle diverse tasks, from technical issues to business process integrations, underlines its importance in the ITSM ecosystem.
Incident management is an IT Service Management (ITSM) component that focuses on identifying, analysing, and resolving IT incidents to maintain business continuity.
This process is vital for quickly restoring interrupted services, reducing the impact on critical services, and ensuring smooth operations.
IT incident management involves several key steps: identification, logging, categorization, prioritisation, investigation, resolution, and closure.
The process includes the identification of incidents, which can range from minor issues like Wi-Fi connectivity problems to significant incidents like service outages.
Once identified, incidents are categorised and prioritised based on their impact on business operations and urgency.
The response to incidents involves investigation, diagnosis, and implementation of a solution, followed by the closure of the incident once the affected service resumes its intended function.
Incident management is not just about solving the incident at hand; it’s about ensuring that similar incidents don’t recur, which is where problem management comes into play.
Problem management aims to identify and address the root causes of incidents to prevent their recurrence, thus differentiating from incident management, which focuses on resolving immediate issues.
Change management plays a role in controlling and coordinating IT systems, services, and infrastructure changes.
This process ensures that changes are introduced, controlled and predictable, minimising the risk of disruption to IT services and business operations.
The primary goal of change management is to reduce the incidents that may arise due to updates, ultimately leading to an improved customer experience and competitive advantage.
The change management process typically includes steps such as change request, assessment, authorization, planning, implementation, evaluation, and closure.
Change management also has a role in enhancing communication and collaboration between IT and other business units, and it plays a significant role in improving service delivery by introducing changes more efficiently and effectively.
Additionally, it helps organisations maintain compliance with industry regulations and standards.
That is why integrating change management practices into IT operations management software can significantly improve the efficiency of change management, provide advanced tools for tracking and analysing the impact of changes, and ensure a smoother transition with minimal disruption to IT services and business operations.
Asset management supports various ITIL processes like change, incident, and problem management.
Effective asset management enhances operational efficiency by accurately tracking assets through various lifecycle stages, from planning and acquisition to utilisation and disposal.
It also provides visibility of assets and their value, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of what assets are owned, their locations, users, and how they are utilised. This information is essential for future planning, budgeting, and decision-making.
Therefore, an essential aspect of asset management is the proactive management of the IT asset lifecycle, which includes stages like planning, procurement, deployment, maintenance, and retirement.
By applying processes across these lifecycle stages, organisations can understand the total cost of ownership and optimise asset usage.
This lifecycle management approach is crucial for reducing costs, managing risks, and supporting decision-making in line with regulatory and contractual requirements.
Moreover, asset management significantly reduces costs by identifying underused or wasted assets that can be reallocated or decommissioned, facilitating better negotiations with suppliers, and preventing asset theft.
Asset management reduces security, regulatory, and technology compliance risks while increasing information security by enabling appropriate asset-based security measures and tracking software lifecycles.
Configuration Management (CM) is about creating a single source of truth by providing visibility into hardware and software composition across the enterprise.
This visibility ensures proper security, service performance, and compliance.
Without CM, organisations lack a clear and complete index of hardware and software, making it challenging to manage configurations and increasing the risk of security vulnerabilities, service disruptions, and non-compliance with regulations.
CM tools store, analyse, and optimise security and resource allocation, enabling network administrators to proactively manage a network’s configuration state and change according to needs.
These tools also play a crucial role in safeguarding the enterprise network and its dependencies, especially in organisations with complex, hybrid infrastructures.
Effective CM must be an all-or-nothing effort, requiring organisations to identify each element, understand its specific configuration details, and manage that data accurately over time.
Challenges in CM include integrating and adopting CM platforms and practices, ensuring data sharing, integrity, and protection, and managing the evolution of data centre technologies.
Service Level Agreements (SLAs), serving as contractual agreements, delineate the expected level of service between a service provider and a customer.
These SLAs are pivotal in ensuring IT services align with business needs and expectations, significantly boosting customer satisfaction and service quality.
Effective SLA management enhances accountability and responsibility in delivering IT services. It establishes a foundation for ongoing improvement and sets realistic expectations.
Monitoring and measuring key performance indicators detailed in the SLA enables IT departments to pinpoint areas needing enhancement, allowing them to proactively refine service quality.
Therefore, key components and best practices in SLAs are critical. Key components of an efficient SLA include defining the service scope, which specifies the services encompassed by the agreement.
Adopting best practices in SLA management within ITSM is essential, such as creating distinct SLAs for each IT service to ensure precise and tailored service management.
Continuous improvement, also known as Continual Service Improvement (CSI) in ITIL, revolves around perpetually assessing and enhancing IT services to align with evolving business objectives and industry standards.
This process entails collecting data, analysing it, and making informed strategic decisions to optimise the effectiveness and efficiency of IT services.
The impact of continuous improvement enables organisations to remain agile and adaptable, proactively identifying improvement areas and implementing changes to enhance service delivery.
This proactive approach helps minimise issues and downtime while increasing customer satisfaction. Without Continuous Improvement, ITSM can become stagnant, leading to outdated practices and ineffective services.
Key concepts of continuous improvement involve collaboration and a focus on identifying opportunities for incremental improvements rather than finding fault. A commonly used approach is the PDCA cycle – Plan, Do, Check, Act.
Benefits of continuous improvement include enhanced overall service quality, decreased resolution times, improved customer satisfaction, reduced costs through greater efficiency, and increased competitive advantage.
Furthermore, implementing ITSM software, such as Jira Service Management, can automate the continuous improvement process, measure the success of initiatives, and increase efficiency.
Several popular frameworks in IT Service Management (ITSM) guide best practices and processes. Among these, ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) stands out as a widely adopted framework.
ITIL provides a comprehensive set of best practices designed to help organisations gain optimal value from IT by aligning IT services with business strategy.
Originating in the 1980s and now managed by Axelos, ITIL has evolved over the years, with the latest version being ITIL 4.
This version adopts a holistic and adaptable approach, emphasizing the importance of collaboration, value focus, and continual improvement.
ITIL is structured around a lifecycle approach, consisting of five stages: Service Strategy, Service Design, Service Transition, Service Operation, and Continual Service Improvement.
This lifecycle provides a framework for managing IT services effectively throughout their entire lifecycle.
The guiding principles of ITIL include focusing on value, starting where you are, progressing iteratively with feedback, collaborating and promoting visibility, thinking and working holistically, keeping it simple and practical, and optimising and automating.
Besides ITIL, other popular ITSM frameworks include COBIT, MOF, eTOM, and TOGAF.
Each framework caters to different organisational needs and offers specific guidelines for IT service management.
For instance, COBIT is designed for governance and information management strategies. At the same time, MOF focuses on the lifecycle of IT services using Microsoft technologies.
These frameworks provide structured methodologies for ITSM, ensuring that IT services are delivered efficiently and aligned with business objectives.
Adopting these frameworks helps organisations improve service delivery, optimise resource utilisation, and foster a culture of continuous improvement in IT services.
ITSM involves the design, implementation, management, and delivery of IT services, and it’s more than just IT support; it’s about delivering IT as a service, aligning with overall business goals.
This holistic approach is vital for seamlessly integrating IT services into business practices.
One key reason ITSM is crucial is its role in aligning IT with business objectives, helping organisations become more efficient and productive.
ITSM reduces the risk of security breaches and leads to significant efficiency gains.
By managing the entire IT service lifecycle, ITSM solutions prevent work disruptions, ensuring that IT teams can focus on their core activities without unexpected interruptions.
ITSM is essential for managing the vast array of technology businesses rely on, from laptops and servers to software applications.
It standardises processes and reduces IT costs by building a predictable and robust IT organisation.
ITSM also mitigates various risks, such as financial and governance risks, and provides actionable IT insights for decision-making.
These benefits are achieved through various ITSM processes, including service level management, change management, incident management, and problem management, which collectively improve the quality of service and ensure compliance.
When we look closely at the key aspects of IT Service Management (ITSM), we see how vital it is for aligning our IT services with our business goals.
It’s all about making sure that your IT operations are not just ticking over but actively supporting our company’s bigger picture and strategies.
This is important for keeping our business processes running smoothly, boosting productivity, and cutting IT costs.
With ITSM, we focus on being service-driven and process-oriented, and we value managerial support, getting everyone on board, clear communication, and structured ways to make things better.
In this context, Octobits emerges as a powerful ally we need for streamlining our ITSM processes.
They’ve got this all-in-one dashboard that makes managing IT service a breeze.
We can get our hands on advanced tools and methods for managing everything ITSM throws at us, from sorting out incidents and changes to handling assets, configurations, and those all-important Service Level Agreements (SLAs).
What’s really cool about Octobits is how their platform is all about continuous improvement.
It’s geared towards making sure IT services keep pace with the ever-changing needs of our business. This means less trouble and downtime and happier customers.
Plus, the platform is user-friendly and packed with features that make it the go-to choice for your businesses to deliver better services, use their resources more wisely, and build a culture where improvement is just part of what we do.
In the end, using Octobits makes the theoretical concept of what is IT service management more practical and easy-used.